Cappadocia - The Magical Land of Nature and History
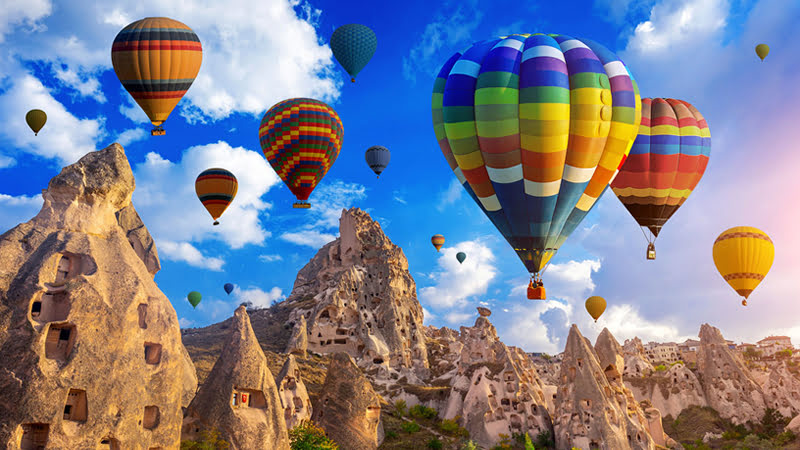

Cappadocia is a fascinating region in the center of Turkiye, covering the provinces of Nevsehir, Kayseri, Aksaray and Nigde. Cappadocia, one of the most impressive touristic regions in the world with its unique geological formations, rich history and cultural heritage, makes its visitors feel like they are in another world.
Cappadocia is one of the most special regions of Turkiye and the world with its natural and cultural beauties. The region's unique geological formations, the fact that it has hosted various civilizations throughout history and its cultural riches make Cappadocia unique. Today, Cappadocia, which hosts millions of visitors every year with its touristic attractions, continues to exist as a magical land that carries the traces of the past and transfers them to the future. This fascinating region is a paradise where nature and history are intertwined and contains many treasures waiting to be discovered.
Let's examine Cappadocia under the titles of geological formations, historical past, cultural riches and touristic attraction.
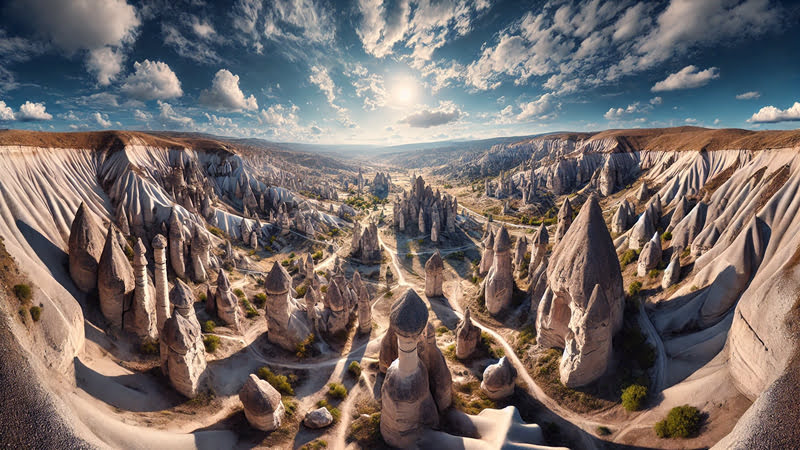
Cappadocia's unique landscape is the result of millions of years of volcanic activity and erosion. The lava and tuff layers erupted by the three main volcanoes in the region, Mount Erciyes, Mount Hasan and Mount Güllü, were shaped by wind and water erosion over time and formed the unique fairy chimneys we see today. Fairy chimneys attract attention with their conical shapes and sometimes rock caps on them.
In addition, the underground cities of Cappadocia are also a part of the geological structure of the region. These underground cities carved into the rocks have been safe areas used as shelters by people throughout history. Derinkuyu and Kaymaklı Underground Cities are the most well-known of these structures and attract attention with their multi-story structures.
Cappadocia has hosted many civilizations throughout history. Various civilizations such as the Hittites, Persians, Romans, Byzantines, Seljuks and Ottomans have played an important role in the history of the region. Cappadocia's strategic location has ensured that it is at the intersection of trade routes throughout history, which has increased the cultural richness of the region.
The first Christian communities in the region fled the persecution of the Roman Empire and took refuge in caves and underground cities in Cappadocia. During this period, churches and monasteries carved into the rocks were built. Göreme Open Air Museum is an important archaeological site where some of these churches have been preserved to this day and are open to visitors.
Cappadocia's cultural richness is not limited to its historical structures. The region's traditional handicrafts, especially pottery, carpet weaving and winemaking, form an important part of Cappadocia's cultural heritage. Avanos is a famous town for pottery, and the handmade pottery made here has become one of the symbols of Cappadocia.
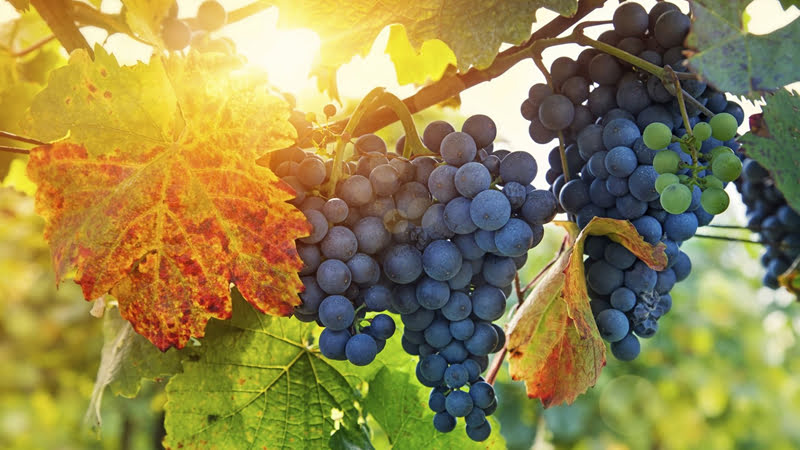
In addition, Cappadocia's grapes and wines are also very famous. The volcanic soil of the region provides ideal conditions for growing grapes, which makes Cappadocia stand out in winemaking. The wineries and vineyards in the region offer visitors the opportunity to taste delicious wines and see the production processes up close.
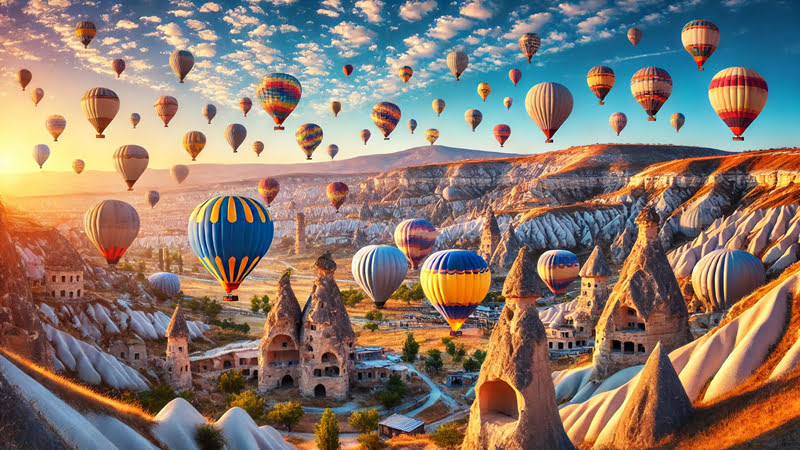
Cappadocia is a paradise for nature and history enthusiasts. Hot air balloon tours among the fairy chimneys offer a unique experience for those who want to see the magnificent view of the region from a bird's eye view. These tours, which are held during sunrise, offer mesmerizing moments where colors and lights dance.
Goreme Open Air Museum, Zelve Valley, Uchisar Castle, Ihlara Valley and Pasabag Priests Valley are among the main tourist attractions of Cappadocia. These areas offer a wide range of options for visitors who want to explore the historical and natural beauties of the region.
Cappadocia has continued to attract touristic attention in recent years. In 2019, the region hosted approximately 3.8 million tourists. Although there was a decrease in the number of visitors in 2020 and 2021, which were the pandemic period, the region started to see intense touristic interest again as of 2022. Today, the annual number of visitors is over 2.5 million, and this number increases every year, revealing the tourism potential of the region. Cappadocia continues to be an indispensable destination for both local and foreign tourists with the unique experiences it offers.
Cappadocia is one of the most special regions of Turkiye and the world with its natural and cultural beauties. The region's unique geological formations, the fact that it has hosted various civilizations throughout history and its cultural riches make Cappadocia unique. Today, Cappadocia, which hosts millions of visitors every year with its touristic attractions, continues to exist as a magical land that carries the traces of the past and transfers them to the future. This fascinating region is a paradise where nature and history are intertwined and contains many treasures waiting to be discovered.
Let's examine Cappadocia under the titles of geological formations, historical past, cultural riches and touristic attraction.
Geological Formations of Cappadocia
Cappadocia's unique landscape is the result of millions of years of volcanic activity and erosion. The lava and tuff layers erupted by the three main volcanoes in the region, Mount Erciyes, Mount Hasan and Mount Güllü, were shaped by wind and water erosion over time and formed the unique fairy chimneys we see today. Fairy chimneys attract attention with their conical shapes and sometimes rock caps on them.
In addition, the underground cities of Cappadocia are also a part of the geological structure of the region. These underground cities carved into the rocks have been safe areas used as shelters by people throughout history. Derinkuyu and Kaymaklı Underground Cities are the most well-known of these structures and attract attention with their multi-story structures.
Historical Background
Cappadocia has hosted many civilizations throughout history. Various civilizations such as the Hittites, Persians, Romans, Byzantines, Seljuks and Ottomans have played an important role in the history of the region. Cappadocia's strategic location has ensured that it is at the intersection of trade routes throughout history, which has increased the cultural richness of the region.
The first Christian communities in the region fled the persecution of the Roman Empire and took refuge in caves and underground cities in Cappadocia. During this period, churches and monasteries carved into the rocks were built. Göreme Open Air Museum is an important archaeological site where some of these churches have been preserved to this day and are open to visitors.
Cultural Riches
Cappadocia's cultural richness is not limited to its historical structures. The region's traditional handicrafts, especially pottery, carpet weaving and winemaking, form an important part of Cappadocia's cultural heritage. Avanos is a famous town for pottery, and the handmade pottery made here has become one of the symbols of Cappadocia.
In addition, Cappadocia's grapes and wines are also very famous. The volcanic soil of the region provides ideal conditions for growing grapes, which makes Cappadocia stand out in winemaking. The wineries and vineyards in the region offer visitors the opportunity to taste delicious wines and see the production processes up close.
Tourist Attractions
Cappadocia is a paradise for nature and history enthusiasts. Hot air balloon tours among the fairy chimneys offer a unique experience for those who want to see the magnificent view of the region from a bird's eye view. These tours, which are held during sunrise, offer mesmerizing moments where colors and lights dance.
Goreme Open Air Museum, Zelve Valley, Uchisar Castle, Ihlara Valley and Pasabag Priests Valley are among the main tourist attractions of Cappadocia. These areas offer a wide range of options for visitors who want to explore the historical and natural beauties of the region.
Cappadocia has continued to attract touristic attention in recent years. In 2019, the region hosted approximately 3.8 million tourists. Although there was a decrease in the number of visitors in 2020 and 2021, which were the pandemic period, the region started to see intense touristic interest again as of 2022. Today, the annual number of visitors is over 2.5 million, and this number increases every year, revealing the tourism potential of the region. Cappadocia continues to be an indispensable destination for both local and foreign tourists with the unique experiences it offers.